A cloud is a visible mass of condensed watery vapor floating in the atmosphere, typically high above the general level of the ground.
This would be the answer you would have gotten a decade ago. Today it is rather: IT Cloud ?
The cloud is a term referring to accessing computer, information technology (IT), and software applications through a network connection, often by accessing data centers using wide area networking (WAN) or Internet connectivity.
Almost all IT resources can live in the cloud: A software program or application, a service, or an entire infrastructure. For example, if a business wanted to build an IT infrastructure, typically it would install the servers, software, and networking resources it needed, but nearly all of those services and resources are now accessible by going to third parties that offer them in the cloud.
Today’s IT related platforms evolve is a very fast pace. We very quickly went from the regular Cloud we mentioned above to Multi-cloud or Hybrid Clouds.
We will find out below what benefits and limits each has.
The multi-cloud is when an enterprise uses more than one cloud platform that each delivers a specific application service. It is not to be confused with Hybrid Cloud that is an infrastructure while multi-cloud is a strategy.
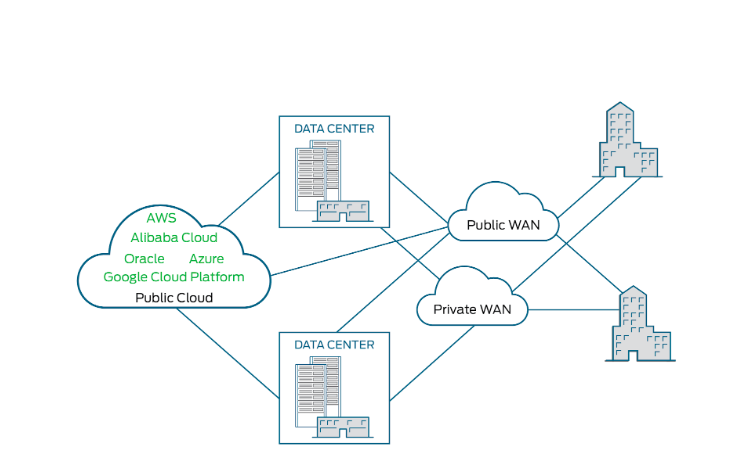
A multi-cloud may use several different architectures, such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), to achieve an overarching business goal. It’s “about using different providers to meet specific workload requirements, and aren’t necessarily connected to each other.”
Companies elect a multi-cloud strategy due to the benefits.
- It’s also customizable and flexible.
- Adopting multi-clouds allow enterprises to escape vendor lock-in as its data is stored on various service providers’ clouds.
- The multi-cloud strategy offers security precautions that a single cloud deployment does not.
- A multi-cloud environment allows groups to comply with IT policy while benefiting from specific cloud technology.”
- Every public cloud provider has strength in some area that outperforms the other competitors, therefore multi-cloud with a combination of the best services from each cloud provider will lead to a better solution. For example, Google cloud platform is the best in Machine learning and AI services that can be integrated with cloud services from other providers.
While the multi cloud’s benefits are very attractive, it does possess some weak points too such as:
- Incorporating a multi-cloud strategy is the potential for a difficult integration across the various cloud servers.
- The multi-cloud also possesses unique security vulnerabilities. While the multi-cloud does limit the debilitating effect of a DDoS attack, it leaves the enterprise vulnerable to other attacks.
- Possessing multiple clouds means that an enterprise can’t apply its firewalls around the multi-cloud in its entirety to stop hackers and viruses.
- An enterprise must maintain due diligence in knowing each of its cloud service providers’ security measures and to then identify the steps it needs to take to secure the gaps in security coverage.
While multi-cloud is a strategy, Hybrid cloud is rather an infrastructure that refers to a mixed computing, storage, and services environment made up of on-premises infrastructure, private cloud services, and a public cloud—such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure—with orchestration among the various platforms. Using a combination of public clouds, on-premises computing, and private clouds in your data center means that you have a hybrid cloud infrastructure.
We mostly speak of these as main advantages for using a hybrid-cloud:
- With hybrid cloud, the organization’s workload is contained within a private cloud while retaining the ability to spontaneously increase their workload and perform the spikes of usage on the public cloud.
- Hybrid cloud has the benefit of being cost effective as organizations pay for the public cloud portion of their infrastructure only when it is needed.
- With hybrid cloud, organization’s workloads get on-premise computational efficiency which ensures maximum workload management.
- You also get highly scalable and flexible designed servers which you can use for yourself and even offer it to a number of individuals so they can also make use of it.
- One of the leading benefits of a hybrid cloud is that you get a centralized private infrastructure on premises.
Hybrid Cloud may have a high number of advantages and although it’s one of the most stable cloud environments, it can still portray a few challenges. These challenges should not be left unattended.
- Although the long-term cost savings are one of the many benefits, the initial deploying cost of a hybrid cloud exceeds as compared to the setup cost incurred in case of a public cloud. While creating a hybrid cloud environment, specific hardware is required to deploy on premises, and that’s what shaves off a large chunk of the budget.
- Hybrid clouds are indeed secure. But it is necessary that precautionary steps are taken by expert IT specialists to ensure the maximum security of data.
- If not picked correctly, cloud compatibility can become a real nuisance for Hybrid Cloud environments.
While these concerns are important to address, if catered in controlled environments, utilizing appropriate experts, and resources, a hybrid cloud can become a total win for your organization.
Almost everything in the digital world is connected to the cloud in some way or another — unless it’s specifically kept in local storage for security reasons. As tech giants and startups find new ways to organize process and present data cloud computing will become a more and more integral part of our lives.
Michael Corrado, World Wide Marketing Manager with Hewlett Packard Enterprise, had very interesting thought on how the future of clouds would be and we are stating him here below:
“The future of cloud computing will most likely represent a combination of cloud based software products and on premises compute to create a hybrid IT solution that balances the scalability and flexibility associated with cloud and the security and control of a private data center.
In the current cloud market the benefits of leveraging the infrastructure of a large cloud provider can be beneficial in many ways. The cost structure works like a utility which provides for an operating expense model with no upfront infrastructure costs.
The ability to scale rapidly works well for companies with high growth demands. With these benefits come some limitations. Your experience is limited by the speed and reliability of your internet connection which can impact your business.
Cloud also introduces additional security concerns in a world where data privacy is increasingly vulnerable. As companies make sense of what is available to them and major technology vendors adjust their business models to allow for flexible consumption payment models to purchase on premises infrastructure, the balance between cloud and in house technology should find its balance.
The variable element of this Hybrid IT future and the most compelling use for cloud will be the software companies that offer their products only as cloud solutions which will diversify a customer’s cloud needs to multiple platforms based on their preferred software vendors.”
Matt Riley, CEO & Co-founder of Swiftype says: “A decade from now, every business will be operating primarily from the cloud, making way for more flexible — yet more productive and efficient — ways of working. Hardware won’t be the problem in a decade — software will.
What is now a ‘budding’ challenge will be full-blown problem in 10 years’ time: the ability to leverage the collective knowledge created in these silos regardless of which service you’re using in the moment. We’re already seeing fragmentation of content and data and it’s posing problems related to organization, search, discovery, and most importantly, collaboration across people/teams/offices/regions/etc.
This is because the trend in successful cloud services is that they solve a specific problem for a specific role/department very well. Large monolithic application suites will become less and less prevalent.
Luckily, we have companies like Swiftype that are trying to solve that today so that it won’t be a big problem in the future. It’s safe to say the only way companies will be able to thrive will be the ones that tackle cloud-born challenges like this head-on.”
With cloud computing and the technology behind it there are many potential opportunities and capabilities. Cloud computing can open a whole new world of jobs, services, platforms, applications, and much more. There are thousands of possibilities beginning to form as the future of cloud computing starts to really take off. Vendors and service providers can get on board to develop new and different ways of selling their goods and services to the cloud users through the cloud technology. It opens up a whole new platform for designers and web developers. Businesses and organizations can organize themselves and conduct business much more affordable and professionally. Social networking and keeping in touch with friends gets a great deal easier as well.